Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hata, Koji*; Niunoya, Sumio*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Miyara, Nobukatsu*
Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 16(2), p.365 - 378, 2024/02
Excavation of underground caverns, such as mountain tunnels and energy-storage caverns, may cause the damages to the surrounding rock as a result of the stress redistribution. In this influenced zone, new cracks and discontinuities are created or propagate in the rock mass. Therefore, it is effective to measure and evaluate the acoustic emission (AE) events generated by the rocks, which is a small elastic vibration, and permeability change. The authors have developed a long-term measurement device that incorporates an optical AE (O-AE) sensor, an optical pore pressure sensor, and an optical temperature sensor in a single multi-optical measurement probe (MOP). Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D activities to enhance the reliability of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) deep geological disposal technology. In a high-level radioactive disposal project, one of the challenges is the development of methods for long-term monitoring of rock mass behavior. Therefore, in January 2014, the long-term measurements of the hydro-mechanical behavior of the rock mass were launched using the developed MOP in the vicinity of 350 m below the surface at the Horonobe Underground Research Center. The measurement results show that AEs occur frequently up to 1.5 m from the wall during excavation. In addition, hydraulic conductivity increased by 2 to 4 orders of magnitude. Elastoplastic analysis revealed that the hydraulic behavior of the rock mass affected the pore pressure fluctuations and caused micro-fractures. Based on this, a conceptual model is developed to represent the excavation damaged zone (EDZ), which contributes to the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-065, 111 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a novel alpha-ray camera consisting of imaging and an energy spectrometer to find the alpha dust to reduce the risk of health damage in decommissioning. We have developed the camera with a position resolution of less than 10  m, and the measurement test for the energy spectra was operated using several alpha-ray sources with an unfolding method.
m, and the measurement test for the energy spectra was operated using several alpha-ray sources with an unfolding method.
Ikeda, Yuji*; Soriano, J. K.*; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.4828_1 - 4828_9, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:98.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Arai, Yosuke*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Tin, Z. H.*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Bareille, C.*; Akebi, Shuntaro*; Kurokawa, Kifu*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Zhang, W.-L.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 21(4), p.410 - 415, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.62(Chemistry, Physical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-044, 58 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop a novel alpha-ray camera consisting of imaging and an energy spectrometer to find the alpha dust to reduce the risk of health damage in Decommissioning. We have developed the camera in FY2020, and the measurement test for the energy spectra. Moreover, the imaging test has been operated. In addition, we have also developed a high-dose-rate monitor system using novel scintillators with red/infra-red emission.
Kuroda, Kenta*; Arai, Yosuke*; Rezaei, N.*; Kunisada, So*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Alaei, M.*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Bareille, C.*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.2888_1 - 2888_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:75.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2019-038, 57 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Imaging System with Ultra-high Spatial Resolution Aiming to Detect Alpha-dust". In the present study, we have developed a prototype of a system aiming to elucidate the behavior of alpha-dust generated at the time of debris retrieval. In this system, alpha-ray is first converted to visible light by novel scintillator. Then, imaging with ultra-high resolution will be possible using a lens and an Si-semiconductor camera (CMOS camera). Also, it will be possible to identify the species of alpha-ray emitting nuclides by unfolding of the spectra. The demonstration tests of the system will be conducted for dust samplers at the Plutonium Fuel Development Center, JAEA. In the development of the present system, it is important to use scintillator whose emission wavelength is sensitive to the CMOS camera as well as high emission scintillator. Considering these conditions, the key technology will be the improvement of the purity of crystals and optimization of the shapes of the materials including powers.
Nakamura, Shoji; Kitatani, Fumito; Kimura, Atsushi; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.493 - 502, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section( )and resonance integral(I
)and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Np(n,
Np(n, )
) Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the
Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the  with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of
with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of  Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A
Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A  -ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of
-ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of  Np,
Np,  Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 186.9
values were derived as 186.9 6.2 barn, and 1009
6.2 barn, and 1009 90 barn, respectively.
90 barn, respectively.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Do, V. K.; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Takamura, Yuzuru*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 155, p.134 - 140, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.96(Spectroscopy)The emission spectra of technetium (Tc) by liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry have been investigated in this study. From the spectra, 52 emission peaks of Tc were observed in the 250-500 nm wavelength range. All peaks were assigned to the neutral state or singly ionized state. The relative intensities of these peaks were similar to those excited by an electric spark. The strongest intensity peaks were found at 254.3 nm, 261.0 nm, and 264.7 nm. Spectral interferences of coexisting elements in highly active liquid waste of reprocessing stream on those three strongest peaks were investigated using simulated sample. No spectral interferences were observed around the 264.7 nm Tc peak. Therefore, analytical performance using 264.7 nm peak was evaluated. The detection limit, estimated on standard and blank samples in 0.4 M nitric acid, was 1.9 mg/L. The relative standard deviation of Tc standard sample (12.0 mg/L) was 3.8% (N = 5, 1 ).
).
 Am-Li sources
Am-Li sourcesHoshi, Katsuya; Nishino, Sho; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011020_1 - 011020_6, 2019/01
We studied the application of AmLi interrogation neutron sources, which originally deployed in non-destructive assay apparatus for nuclear safeguard, to calibration work. To determine the emission rate, the angular distribution of neutron fluence was measured by a potable long counter. The emission rate at the date of measurement (October 23rd, 2015) was determined to be 1.00 10
10 n/s (
n/s ( 4.1% (
4.1% ( = 2)).
= 2)).
Do, V. K.; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Takamura, Yuzuru*; Surugaya, Naoki; Kuno, Takehiko
Talanta, 183, p.283 - 289, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.53(Chemistry, Analytical)We develop a novel analytical method employing liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry for measurement of total cesium in highly active liquid wastes. Limit of detection and limit of quantification are 0.005 mg/L and 0.02 mg/L, respectively. The method is validated and applied to the real samples.
Kuroda, Kenta*; Ochi, Masayuki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Bareille, C.*; Akebi, Shuntaro*; Kunisada, So*; Muro, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 120(8), p.086402_1 - 086402_6, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:91.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary) emission reduction goal in 2050
emission reduction goal in 2050Kamiji, Yu; Suzuki, Koichi*; Yan, X.
JAEA-Technology 2016-010, 24 Pages, 2016/07
Japanese government has set the goal of reducing CO emission by 26% in 2030 below the 2013 level, in longer term, by 80% below the 1990 level. To achieve the goals, various measures should be taken. The GTHTR300, a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) design being developed by JAEA offers spectrum of heat applications by using its high temperature heat up to 950
emission by 26% in 2030 below the 2013 level, in longer term, by 80% below the 1990 level. To achieve the goals, various measures should be taken. The GTHTR300, a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) design being developed by JAEA offers spectrum of heat applications by using its high temperature heat up to 950 C. The potential contribution of CO
C. The potential contribution of CO emission reduction by HTGR is estimated considering domestic and overseas deployment of the GTHTR300. The best estimate for domestic CO
emission reduction by HTGR is estimated considering domestic and overseas deployment of the GTHTR300. The best estimate for domestic CO reduction is 2.07
reduction is 2.07 10
10 ton- CO
ton- CO /yr and that from oversea is 2.25
/yr and that from oversea is 2.25 10
10 ton- CO
ton- CO /yr. The sum of these is about 47% of 9.13
/yr. The sum of these is about 47% of 9.13 10
10 ton- CO
ton- CO /yr which is CO
/yr which is CO reduction target in 2050, for which deployment of 52 plants in Japan and 113 plants abroad, with each plant containing four 600 MWt reactor units, is required.
reduction target in 2050, for which deployment of 52 plants in Japan and 113 plants abroad, with each plant containing four 600 MWt reactor units, is required.
Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; Hirose, Ryoichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 106(12), p.121109_1 - 121109_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.07(Physics, Applied)Yamamoto, Kazami; Shibata, Takeo*; Ogiwara, Norio; Kinsho, Michikazu
Vacuum, 81(6), p.788 - 792, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:46.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The J-PARC 3GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) is required to provide 1MW pulsed protons to the spallation neutron target and the 50 GeV main ring. Since the acceleration period is set at a repetition rate of 25Hz, the eddy current effect due to such rapid repetition magnetic field is a big issue (i.e. the perturbation of the magnetic field and the heating owing to the ohmic loss) in the metal duct. Therefore, we choose the ceramics duct in the magnets in order to avoid the eddy current effect. But the total secondary electron emission yield (SEY) from the ceramics surface is larger than the metal one. In order to reduce these undesirable electron emitted from the chamber surface, Titanium Nitride (TiN) is coated on the inside surface of the chambers. We measured SEY from TiN coating surface with various conditions. We further investigated Diamond Like Carbon coating to search the possibility of another coating. The results of these measurements are shown.
 Au surfaces with a hyperthermal O
Au surfaces with a hyperthermal O molecular beam
molecular beamOkada, Michio*; Moritani, Kosuke; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Mizutani, Hironori*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
Surface Science, 600(18), p.4228 - 4232, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:64.46(Chemistry, Physical)Dissociative adsorption of hyperthermal O molecules on Cu
molecules on Cu Au(100) was investigated by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with a synchrotron light source. Comparing the O-uptake curve on Cu
Au(100) was investigated by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with a synchrotron light source. Comparing the O-uptake curve on Cu Au with that on Cu, it was found that the dissociative adsorption of O
Au with that on Cu, it was found that the dissociative adsorption of O is more activated (less reactive) due to Au alloying. The low-energy electron-diffraction (LEED) pattern of c(2
is more activated (less reactive) due to Au alloying. The low-energy electron-diffraction (LEED) pattern of c(2 2) for the clean surface turned into the (1
2) for the clean surface turned into the (1 1) LEED pattern during the oxidation by hyperthermal O
1) LEED pattern during the oxidation by hyperthermal O molecular beam, suggesting that the O adsorption induces the Cu-atom segregation on the surface.
molecular beam, suggesting that the O adsorption induces the Cu-atom segregation on the surface.
 film formed by a hyperthermal O-atom beam at room temperature
film formed by a hyperthermal O-atom beam at room temperatureTagawa, Masahito*; Sogo, Chie*; Yokota, Kumiko*; Hachiue, Shunsuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 44(12), p.8300 - 8304, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.82(Physics, Applied)Si oxide layers formed on Si(001) substrates by irradiation of hyperthermal oxygen atomic beams at room temperature were analysed at the JAERI soft X-ray beamline by photoemission spectroscopy. It was found that sub-oxide components were scarcely observed in the Si oxide layers formed by the atomic oxygen beam.
 emission spectroscopy of layered manganate La
emission spectroscopy of layered manganate La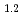 Sr
Sr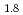 Mn
Mn O
O
Agui, Akane; K
 mbre, T.*; S
mbre, T.*; S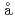 the, C.*; Nordgren, J.*; Usuda, Manabu; Saito, Tomohiko*; Moritomo, Yutaka*
the, C.*; Nordgren, J.*; Usuda, Manabu; Saito, Tomohiko*; Moritomo, Yutaka*
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 144-147, p.589 - 592, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.68(Spectroscopy)Current research in the perovskite and layered perovskite-type manganese oxides has expanded to include the study of electronic and magnetic properties such as the colossal magnetoresistance (CMR), orbital ordering and charge ordering. The O K soft X-ray emission and absorption spectra (XES and XAS) of La
soft X-ray emission and absorption spectra (XES and XAS) of La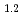 Sr
Sr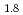 Mn
Mn O
O were measured at selected excitation energies in order to investigate the electronic structure. The measurements were carried out by using a soft X-ray emission spectrometer at beamline BW3 at HASYLAB, Germany. The dependence of O K
were measured at selected excitation energies in order to investigate the electronic structure. The measurements were carried out by using a soft X-ray emission spectrometer at beamline BW3 at HASYLAB, Germany. The dependence of O K XES on excitation-energy was observed. It is attributed the different site of oxygen ions.
XES on excitation-energy was observed. It is attributed the different site of oxygen ions.
Nath, K. G.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 144-147, p.323 - 326, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.35(Spectroscopy)The effect of laser annealing on electronic atructures and molecular orientation for poly(dimethylsilane), {PDMS, [Si(CH )
) ]
] } has been studied by synchrotron radiation photoemission and photoabsorption spectroscopy. Prior to annealing, PDMS powder was mounted on the basal plane of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite. Both Si 1s X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy at Si 1s edge show that electronic structures have been modified due to annealing. Furthermore, the angle-dependent NEXAFS spectra clearly indicate that the annealed products maintain a specific orientation. Interestingly, no such kind of orientation is present in as-received PDMS powder as no angle-dependency is observed before annealing.
} has been studied by synchrotron radiation photoemission and photoabsorption spectroscopy. Prior to annealing, PDMS powder was mounted on the basal plane of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite. Both Si 1s X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy at Si 1s edge show that electronic structures have been modified due to annealing. Furthermore, the angle-dependent NEXAFS spectra clearly indicate that the annealed products maintain a specific orientation. Interestingly, no such kind of orientation is present in as-received PDMS powder as no angle-dependency is observed before annealing.
Koura, Hiroyuki
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.38, P. 9, 2005/05
We calculate proton-emission partial half lives and discuss dominant decay modes in the heavy and superheavy nuclidic region. The proton-emission partial half-lives are calculated from the one-dimensional WKB method with single-proton potentials and a mass formula that our group has developed. The calculated half lives well reproduce experimental ones in order of 100 or 1/100 which is similar predictability to other predictions as the alpha decay and the beta decay. We apply this result to calculation of branching ratios of nuclear decays considered the alpha decay, beta decay and spontaneous fission in the heavy and superheavy nuclide region. In this analysis we point out that proton-emitting nuclei are expected to be in the unknown proton-rich nuclidic region with 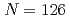 . On the other hand, proton-rich nuclei with
. On the other hand, proton-rich nuclei with 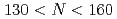 have much shorter spontaneous-fission half-lives than ones of proton emissions on this calculation, therefore we conclude that ground-state proton emissions would not occur in that region.
have much shorter spontaneous-fission half-lives than ones of proton emissions on this calculation, therefore we conclude that ground-state proton emissions would not occur in that region.